For any vehicle owner, maintaining the heart of your automobile is crucial for ensuring a long and trouble-free driving experience. Among the numerous components that require attention, the timing belt stands out as particularly significant. This vital piece of engine equipment demands proper understanding and maintenance to avoid potentially catastrophic engine damage and costly repairs. Let’s explore the essentials of timing belt care that every motorist should know.
The Vital Role of Timing Belts in Engine Performance
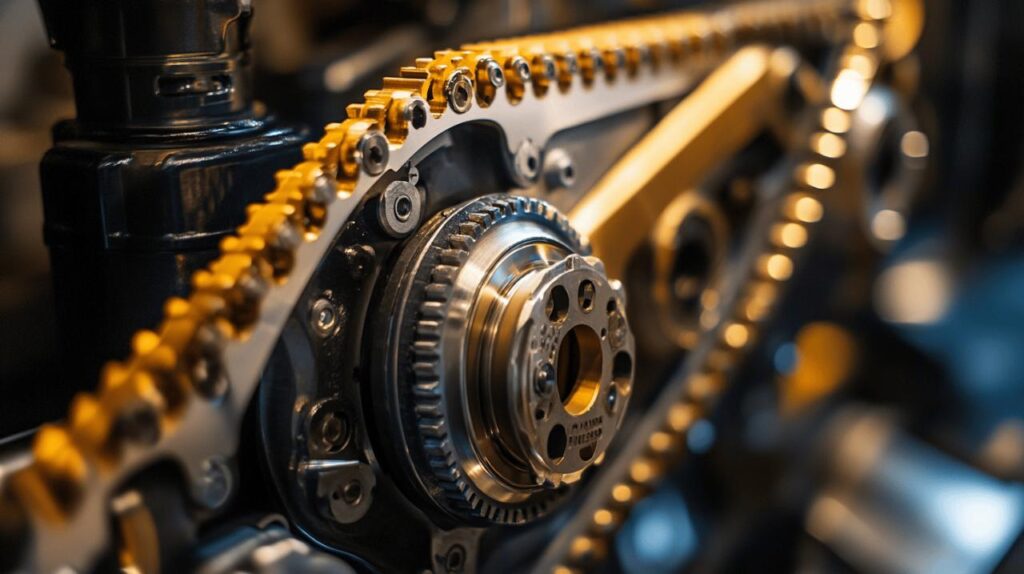
The timing belt, also commonly referred to as a cambelt, performs a critical function in your vehicle’s engine operation. This unassuming component is responsible for synchronising the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft in your engine, ensuring that the valves open and close at precisely the right moments during the combustion process. Motor Publish automotive experts emphasise that without this perfect synchronisation, your engine simply cannot function properly, potentially leading to significant mechanical problems.
How timing belts synchronise engine components
The timing belt works as a sophisticated conductor, orchestrating the movement between various engine parts. When functioning correctly, it ensures that the intake and exhaust valves open and close in perfect harmony with the movement of the pistons. This synchronisation is what allows fuel to enter the combustion chamber and exhaust gases to exit at exactly the right moment. The precision of this timing directly impacts your engine’s efficiency, power output, and fuel economy, making the timing belt far more important than its simple appearance might suggest.
Signs of Timing Belt Wear and Potential Consequences
Recognising the warning signs of a deteriorating timing belt can save you from serious engine damage. Be alert for symptoms such as unusual ticking or squealing noises coming from the engine, difficulty starting your vehicle, rough idling, or engine misfires. You might also notice a loss of power during acceleration or unexpected engine overheating. These signs should never be ignored, as the consequences of a timing belt failure can be severe. When a timing belt breaks while driving, the engine will immediately stop running, potentially leaving you stranded. More concerning is that in many engines, the pistons and valves can collide, causing extensive and expensive internal engine damage that might cost thousands of pounds to repair.
Timing belt replacement intervals and best practices
 Proactive replacement of your timing belt according to manufacturer guidelines is the most effective way to prevent the catastrophic consequences of belt failure. Unlike other maintenance items that can sometimes be stretched beyond recommended intervals, timing belt replacement should be treated as a non-negotiable service point in your vehicle’s maintenance schedule.
Proactive replacement of your timing belt according to manufacturer guidelines is the most effective way to prevent the catastrophic consequences of belt failure. Unlike other maintenance items that can sometimes be stretched beyond recommended intervals, timing belt replacement should be treated as a non-negotiable service point in your vehicle’s maintenance schedule.
Manufacturer guidelines for timing belt replacement
Most vehicle manufacturers recommend replacing the timing belt every 60,000 to 100,000 miles or every 5 to 10 years, whichever comes first. However, these intervals can vary significantly between different makes and models. For instance, Volkswagen typically recommends replacement every 60,000 to 90,000 miles, while some Honda models specify a 7-year interval regardless of mileage. The replacement cost also varies widely across different brands, ranging from approximately £300 for some Toyota models to over £1,000 for certain BMW vehicles. These figures include both parts and labour, which explains the significant variation in pricing. The average cost across all makes tends to hover around £468, though your specific vehicle may fall above or below this figure.
Factors that affect timing belt lifespan
Several factors can influence how long your timing belt will last, potentially shortening its service life below the manufacturer’s recommended interval. Extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, can accelerate wear and tear on the belt material. Frequent short trips that don’t allow the engine to reach optimal operating temperature can also contribute to premature aging. Interestingly, even vehicles with low mileage can experience timing belt issues if the car is older, as the belt material can deteriorate simply from age. Some modern vehicles use wet timing belts that operate inside the engine and are lubricated by oil. These require special attention to oil quality and levels, as improper lubrication can lead to accelerated wear. Ford suggests these wet belts should last up to 144,000 miles, while Vauxhall recommends replacement at just 60,000 miles, highlighting the importance of consulting your specific vehicle’s manual rather than following general advice.

